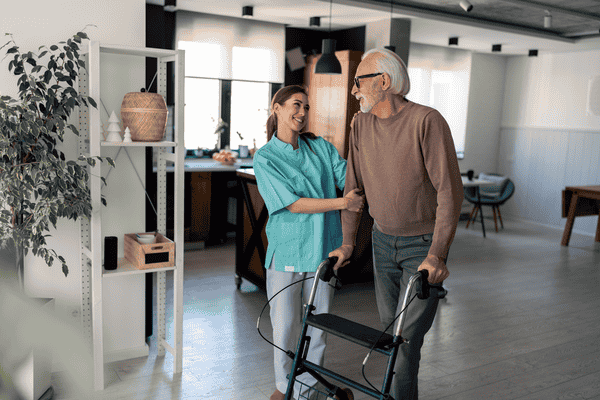
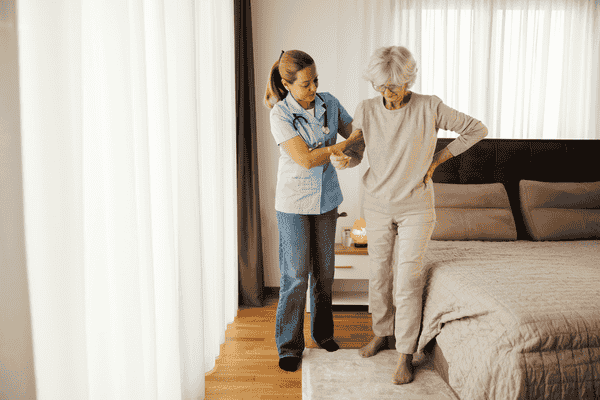
Are you looking for ways to support your older family members with mobility challenges but not sure where to start? Picture this: your grandmother struggles to navigate her home, once filled with cherished memories, now feeling like an obstacle course. It’s moments like these that underline the importance of providing proper assistance to seniors facing mobility issues. As a family caregiver or concerned individual, understanding how to best assist your loved ones is crucial to their safety and well-being.
In our blog, “The Essential Guide to Assisting Seniors with Mobility Challenges,” we’ll delve into practical strategies and invaluable insights tailored to help you navigate the complexities of senior mobility assistance. From essential tips on creating a comfortable living environment to exploring relevant government programs and resources, this guide will empower you to provide the care and support your senior family members deserve.
Get ready to embark on a journey toward ensuring the independence and comfort of your loved ones, as we equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to make a positive difference in their lives.
Introduction to Providing Mobility Assistance to Seniors
As seniors age, they may encounter various challenges that affect their mobility. The ability to move independently is crucial for their overall well-being and quality of life. This is where caregivers play a vital role in providing the necessary assistance and support to help seniors maintain their independence and navigate the obstacles presented by mobility issues.
Mobility assistance encompasses a wide range of activities, including helping seniors with tasks such as walking, transferring, and using assistive devices like wheelchairs or walkers. Caregivers not only provide physical support but also serve as emotional and mental pillars for seniors, fostering their sense of security and well-being.
By offering mobility assistance, caregivers ensure that seniors can continue engaging in daily activities, maintaining a fulfilling social life, and preserving their physical health. The goal is not merely to help seniors navigate their surroundings but also to encourage their independence, allowing them to lead an active and fulfilling lifestyle.
In the following sections, we will explore the challenges faced by seniors with limited mobility, provide practical tips for caregivers, discuss home modifications to enhance safety and accessibility, and explore government programs and support available for seniors with mobility issues. Through this comprehensive caregiver’s guide, you will gain valuable insights and strategies to assist your loved ones in maintaining their independence and improving their overall quality of life.
Understanding the Challenges of Senior Mobility
As seniors age, they may experience various mobility challenges that can significantly impact their daily lives. Understanding these challenges is crucial for caregivers to provide effective assistance and ensure the well-being and independence of their loved ones. Here, we will explore common mobility issues faced by seniors and the factors that contribute to them.
Difficulties with Balance, Strength, and Coordination
One of the primary challenges seniors face is maintaining balance. As we age, our sense of balance tends to deteriorate, making seniors more susceptible to falls and injuries. This can be attributed to age-related changes in the inner ear, which affects our balance mechanism.
Furthermore, a decrease in muscle strength and coordination can make it challenging for seniors to perform routine activities. Loss of muscle mass, known as sarcopenia, is a common age-related condition that contributes to reduced strength and mobility. These physical changes can affect a senior’s ability to walk, stand, or carry out daily tasks.
Impact of Age-Related Conditions and Chronic Illnesses
Age-related conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and degenerative joint diseases can significantly impede mobility in seniors. Arthritis, a condition characterized by joint inflammation, often leads to pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. For seniors with arthritis, simple movements like walking or gripping objects can become painful and challenging.
Chronic illnesses, such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke, can also result in mobility problems. These conditions often cause muscle weakness, impaired coordination, and difficulty with balance control. Seniors with Parkinson’s disease, for example, may experience tremors and stiffness, hindering their ability to move freely.
Additionally, the presence of cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease or peripheral artery disease, can impact mobility. Reduced blood flow to the limbs can lead to leg pain while walking, known as claudication, making it difficult for seniors to engage in physical activities.
Understanding these challenges is essential for caregivers to provide appropriate support and assistance to seniors with mobility issues. By recognizing the underlying factors contributing to their limited mobility, caregivers can implement strategies and interventions that help seniors maintain their independence and improve their quality of life.
Remember, each senior’s mobility challenges are unique, and it is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized care plan that addresses their specific needs.
Creating a Safe and Accessible Environment
As a caregiver, making necessary adaptations and modifications to the home environment is crucial for enhancing senior mobility and ensuring their safety and independence. By implementing home safety measures, utilizing assistive devices, and making targeted home modifications, you can create a supportive living space for your loved ones with limited mobility.
Home Safety Measures
- Clear Clutter: Remove any unnecessary objects and ensure clear pathways throughout the house to minimize the risk of falls or accidents.
- Adequate Lighting: Install bright, well-placed lighting throughout the home to improve visibility and prevent tripping hazards. Consider motion-sensor lights in common areas.
- Secure Rugs and Mats: Use nonslip mats or secure rugs with double-sided tape to prevent seniors from slipping or tripping.
- Handrails and Grab Bars: Install handrails along staircases and in bathrooms to provide support and stability. Grab bars in the shower and near the toilet can significantly reduce the risk of falls.
- Avoid Slippery Surfaces: Use slip-resistant flooring in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and kitchens, to prevent accidents.
Assistive Devices
- Mobility Aids: Depending on the individual’s needs, consider providing mobility aids such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs to assist with stability and movement.
- Transfer Aids: Implement transfer aids like transfer benches or sliding boards to help seniors move safely between different surfaces, such as from bed to wheelchair or from wheelchair to shower.
- Reachers and Grabbers: These tools can help seniors reach items without the need for excessive bending or stretching, reducing the risk of falls.
- Shower Chairs or Benches: Provide a sturdy, nonslip chair or bench in the shower to enable seniors to bathe in a seated position, ensuring comfort and safety.
- Raised Toilet Seats: Install raised toilet seats to make it easier for seniors to sit down and stand up, minimizing strain on their joints.
Home Modifications
- Ramps and Handicap Access: Install ramps or lifts at entry points to eliminate barriers for seniors with mobility aids. Ensure doorways are wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs.
- Bathroom Modifications: Consider installing walk-in showers or bathtub modifications like grab bars, handheld showerheads, and adjustable-height shower seats for added safety and convenience.
- Stair Lifts: If there are multiple levels in the home, consider installing stair lifts to allow seniors to navigate the stairs safely and comfortably.
- Grab Bars Throughout the House: Besides bathrooms, strategically place grab bars in hallways and other relevant areas to provide additional support.
- Floor-Level Changes: Minimize trip hazards by using smoothly transitioned flooring material at floor-level changes, such as from carpet to tile or hardwood.
Remember to consult with professionals, such as occupational therapists or home modification specialists, to ensure the modifications align with the specific needs of your loved ones. By creating a safe and accessible environment, you can empower seniors with limited mobility to navigate their homes with confidence and maintain their independence.
Conclusion: Empowering Caregivers and Seniors Alike
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, it is important to remember that assisting seniors with mobility challenges requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the common mobility issues seniors face, creating a safe and accessible environment, and leveraging available government programs and resources, caregivers can significantly enhance the quality of life for their loved ones.
Ultimately, the goal is to empower both caregivers and seniors, fostering a sense of independence and well-being. With the right knowledge and tools, caregivers can navigate the complexities of senior mobility assistance and provide the care and support that their loved ones deserve.
In this journey, always remember the importance of patience, compassion, and understanding. Each senior’s experience with mobility challenges is unique, and a personalized approach is essential. By working closely with healthcare professionals and utilizing available resources, caregivers can make a positive difference in the lives of their loved ones, ensuring they live with dignity, independence, and happiness.