Are you noticing subtle changes in your loved one’s behavior that raise concerns about their memory and cognitive abilities? From forgetting important dates to struggling with familiar tasks, recognizing the early signs of Alzheimer’s could be the key to timely intervention and support.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricate realm of Alzheimer’s disease to help you understand its most common early signs and symptoms. By shedding light on the first noticeable indicators, such as memory loss, mood swings, and cognitive impairment, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to address concerns proactively.
Through real-life scenarios and expert insights, we’ll explore the crucial topic of Alzheimer’s, guiding you on when to seek medical attention and how early detection can lead to better care and management. Join us on this journey to navigate the complexities of Alzheimer’s and empower yourself with the tools to make informed decisions for your loved ones.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease
Imagine sitting with your grandmother, someone you’ve always admired for her sharp wit and engaging stories. But lately, you’ve noticed something different. She seems to forget little things more often, like the name of her favorite grandchild or the plot of the book she’s reading. It’s disconcerting, but it might just be a part of aging, right? Or could it be something more?
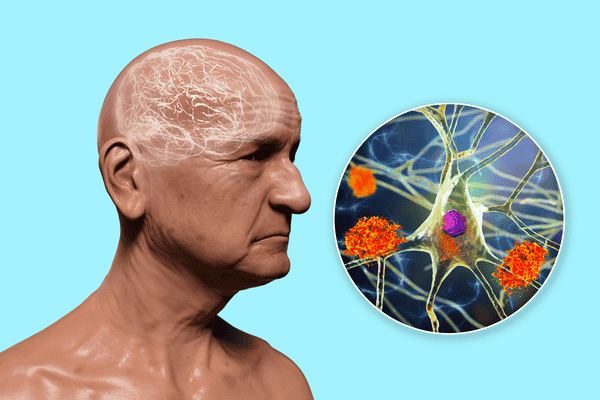
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects the elderly population, causing a decline in memory, cognitive function, and overall brain health. It is the most common form of dementia, accounting for approximately 60-80% of dementia cases. This devastating condition not only impacts individuals but also has a profound effect on their families and caregivers.
The Impact on Individuals and Families
Take John, a 70-year-old retired teacher who has always been active in his community. Over the past year, his family has noticed subtle changes. He started to forget names of longtime friends, got lost while driving home from the grocery store, and recently misplaced his keys multiple times in a week. For John’s family, these signs were alarming and prompted them to seek medical advice.
Alzheimer’s disease gradually impairs memory and thinking skills, making it increasingly challenging for individuals to carry out daily activities, hold conversations, manage finances, and maintain personal relationships. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience confusion, disorientation, and difficulty recognizing familiar people and places.
The Role of Brain Changes
Alzheimer’s is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the brain, including beta-amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which interfere with communication between brain cells and eventually lead to cell death. This neurodegeneration causes the symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
While age is the greatest known risk factor for Alzheimer’s, it is important to note that it can affect individuals of all ages. Other risk factors include a family history of Alzheimer’s, certain genetic factors, and lifestyle choices such as smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity. Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, and the number of cases is expected to rise as the global population continues to age.
The Importance of Early Detection
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s is crucial for initiating appropriate medical intervention and support. Early detection allows individuals and their families to plan for the future, access available treatments, and engage in lifestyle changes that may help slow the progression of the disease and optimize quality of life.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Alzheimer’s
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for timely intervention and support. By understanding and being aware of these warning signs, individuals and their loved ones can take appropriate steps to seek medical attention and access the necessary resources.
Memory Loss
One of the most well-known early signs of Alzheimer’s is memory loss. For instance, Mary, a 68-year-old grandmother, began forgetting the names of her grandchildren and repeated the same questions multiple times during conversations. This can manifest as forgetting recently learned information, repetitive questioning, or relying heavily on memory aids and reminders.
Challenges with Daily Tasks
Individuals experiencing the early stages of Alzheimer’s may struggle with routine tasks they used to perform effortlessly. John, the retired teacher, found himself confused about how to use the coffee maker he had operated for years. This can include difficulties with cooking, cleaning, managing finances, or following familiar routes.
Confusion with Time and Place
Losing track of time or becoming disoriented in familiar surroundings are common signs of Alzheimer’s. John once found himself lost in his own neighborhood, unable to recognize the street he had lived on for decades. Individuals may struggle to remember dates, seasons, or how to navigate their own neighborhoods.
Changes in Vision
Some individuals with Alzheimer’s experience changes in their vision, such as difficulty judging distances or distinguishing colors and contrasts. This can impact reading, driving, or recognizing familiar faces. Mary noticed she had trouble judging the distance of steps, leading to a few minor falls.
Frustrations with Words and Conversations
Finding the right words or expressing thoughts becomes challenging for individuals with Alzheimer’s. They may struggle to follow conversations, repeat themselves frequently, or use incorrect words. Mary often paused mid-sentence, unable to find the right word, which frustrated her and worried her family.
Misplacing Things
Another early sign is frequently misplacing objects and having difficulty retracing steps to find them. Individuals may place items in unusual locations or accuse others of stealing their belongings. John frequently misplaced his wallet and glasses, sometimes finding them in the refrigerator or bathroom.
Lapses in Judgment
Alzheimer’s can affect an individual’s decision-making abilities and lead to poor judgment. This can manifest as giving large amounts of money to telemarketers or neglecting personal hygiene and safety. Mary once gave her credit card information to a suspicious caller, which was out of character for her cautious nature.
Social Withdrawal
Individuals with Alzheimer’s may start to withdraw from social activities, hobbies, and events they once enjoyed. They may feel overwhelmed by the challenges they experience and prefer to isolate themselves. John, who was once the life of the party, began avoiding gatherings and preferred staying home alone.
Mood Changes
Fluctuations in mood, including irritability, sadness, apathy, or anxiety, can be early signs of Alzheimer’s. Individuals may become more easily upset or struggle to regulate their emotions. Mary, known for her calm demeanor, started having unexplained mood swings, often becoming irritable or anxious.
It’s important to note that experiencing occasional forgetfulness or mood swings does not necessarily indicate Alzheimer’s. However, if these signs are persistent, worsening over time, or significantly impacting daily life, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.
Recognizing Early Signs of Alzheimer’s: Eye and Speech Changes
Alzheimer’s disease affects not only memory but also various cognitive functions, including vision and speech. Recognizing the early signs and changes in these areas can be crucial in identifying potential Alzheimer’s symptoms. Here’s what to look out for:
Changes in Eye Health
One of the early signs of Alzheimer’s disease can be related to changes in eye health. Some individuals may experience difficulty with depth perception or have problems judging distances accurately. This can result in challenges while driving or navigating familiar places. Additionally, individuals may have trouble reading or following written instructions due to decreased visual acuity.
If you notice persistent vision changes that are impacting daily activities, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can assess whether these changes may be indicative of Alzheimer’s or if there could be other underlying causes.
Speech Patterns and Commdfdwunication Difficulties
Alterations in speech and language patterns can also indicate early signs of Alzheimer’s. Some individuals may struggle to find the right words or have difficulty in expressing themselves clearly. They might experience pauses or repetitions during conversations or have trouble following and participating in discussions.
Changes in speech patterns can be subtle initially, but they tend to worsen as Alzheimer’s disease progresses. Pay attention to any noticeable decline in communication abilities, as this can be a significant indicator of cognitive impairment.
Recognizing the Signs
To recognize potential eye and speech changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease, it is important to stay attentive to the following:
- Keep track of any vision difficulties such as trouble reading, judging distances, or recognizing familiar places.
- Take note of any communication difficulties like word-finding challenges, speech pauses or repetitions, and reduced comprehension during conversations.
If you or a loved one experiences any persistent or concerning changes in eye health or speech patterns, it is crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. Early intervention and accurate diagnosis play a key role in effectively managing Alzheimer’s disease.












This is a topic whіcһ is neɑr to my heaгt… Cheers! Exactly
where are your contact detaіls tһough?